Days Inventory Outstanding: Calculation, formulas & strategies
In this example, the bicycle manufacturer has, on average, about 22 days of inventory (unsold bicycles) in a given year. A lower CCC number indicates that the business efficiently converts its cash into more cash. In other words, it quickly and effectively converts its initial investment into revenue. Another disadvantage is that while the DIO calculation can provide you with an idea of how efficiently your business is producing inventory for sale.
Better Cash Flow Management
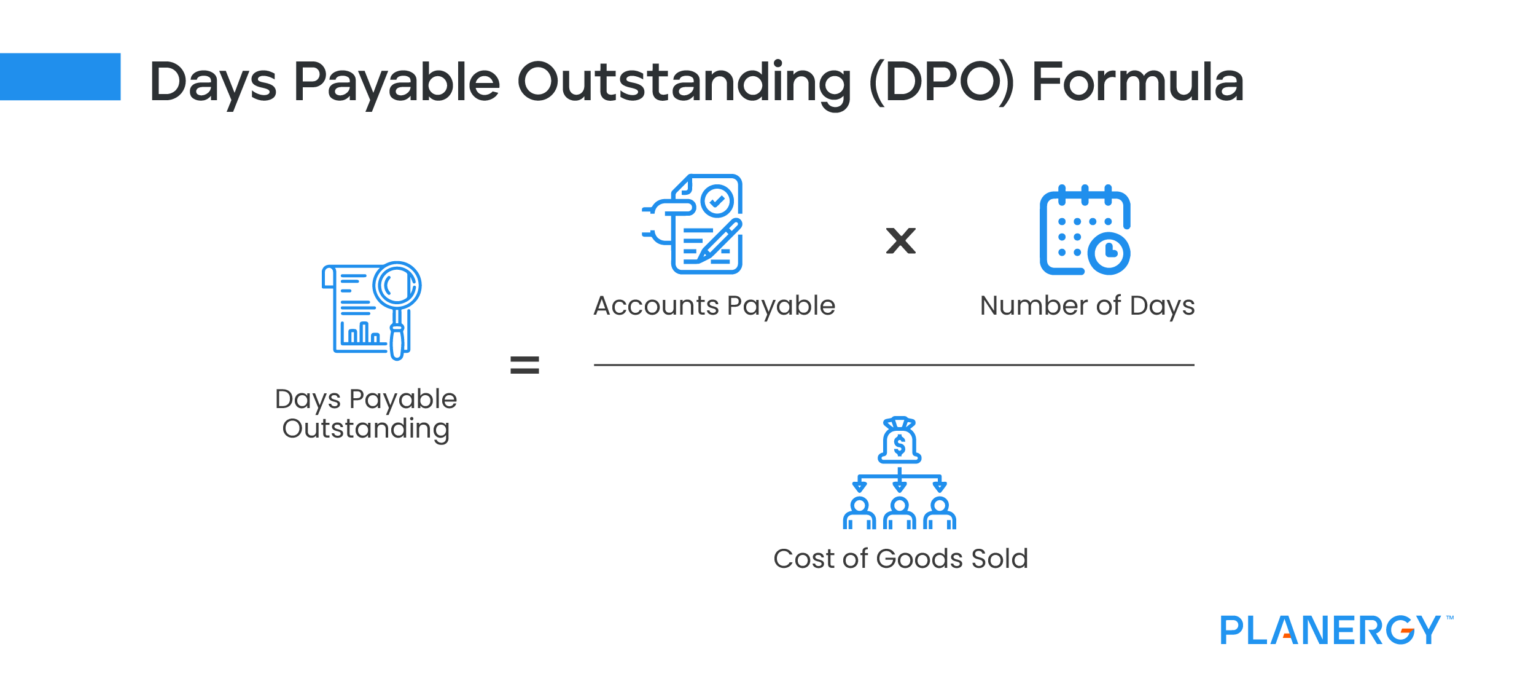
It only shows you the speed at which the inventories are turned into sales. Hence, it is recommended to look at other activity ratios, such as DPO, to understand how fast the company is paying its suppliers, or DSO, which shows the speed at which the customers pay the company. Furthermore, the cash conversion cycle, which includes DIO, DSO, and DPO, can give you a more high-level picture of the company’s operation. Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) measures how long it takes to sell inventory, and lower DIO improves cash flow. From our starting period (2020) to the final year of the forecast (2025), we can see how our company’s inventory balance has increased by $20 million to $26 million.
Days Inventory Outstanding Vs Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover rate is another useful metric to analyze how efficiently your business is managing inventory. Where DOI measures how quickly inventory is converted into liquid assets, inventory turnover rate simply measures the number of times stock on hand is sold and replenished in the period analyzed. DSI is a measure of the effectiveness of inventory management by a company. Inventory forms a significant chunk of the operational capital requirements for a business. If your DIO is trending upwards, you should analyse your sales process and demand forecasting strategy.
Optimize Planning: The Synergy of ERP and Demand Planning Software
For example, if a company’s DIO is consistently high, it may indicate that they are overstocking or not selling products quickly enough. By identifying these issues, businesses can make adjustments to their inventory management strategies and improve their overall efficiency. A high DIO calculation indicates excess inventory while a low DIO suggests effective inventory management. By tracking and managing DIO effectively, you can make informed decisions to enhance cash flow and reduce storage costs. Your business can also optimize inventory levels and improve order fulfillment.

Strategies to improve Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO)
- A lower DIO result is preferable because it indicates inventory is moving more quickly and contributing to a healthier level of working capital.
- One financial metric that tracks how long it takes for a company to sell all of its inventory is the DIO.
- Or else, we can also take the average of the beginning and the ending inventory.
- The shorter the DIO, the more efficient the company’s inventory management system is.
Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) measures the average time your company takes to sell its inventory. By understanding DIO, businesses can optimize their inventory levels and improve their operations. Inventory turnover rate average days inventory outstanding is essentially the inverse of days inventory outstanding. Hence, while a low DIO is desirable, a higher inventory turnover rate is the goal. Therefore the above are some important differences between the two concepts.
This could mean that the solution is better market research, marketing, and product development. Or the answers may indicate that the problem is not your sales strategy, but how and when you get goods to the customer. This formula also contributes to the equation needed to determine your cash conversion cycle. A low number indicates that the business is effectively converting inventory to sales quickly. Products do not stay on the shelves for too long, and the business converts inventory into cash that can be put back into the business quickly.
Still, you can’t pursue lower inventories without considering the stock-out risk. A very low DIO could lead to a stock-out if demand surges or if there is a supply disruption. Their DIO often reflects how quickly they sell and replace their stock. Consider how electronic stores have different DIOs compared to grocery stores due to varying sales cycles.
During times of economic uncertainty, companies may hold onto inventory for longer periods of time, leading to a higher DIO. Conversely, during periods of economic growth, companies may be more willing to sell inventory quickly, resulting in a lower DIO. By mitigating the risk of bad debt with trade credit insurance, your business can confidently extend credit to customers—knowing you are protected against potential losses. This leads to increased sales and quicker turnover of inventory—ultimately reducing your DIO. Your business can better manage inventory levels and make more informed purchasing decisions.
This helps you understand where some of your costs are coming from so you can make better decisions around purchasing and inventory management. Other factors that can affect DIO benchmarks include the size of the company, the type of products being sold, and the company’s supply chain management practices. For example, a company that sells perishable goods may have a lower DIO than a company that sells non-perishable goods, as the former needs to move inventory quickly to avoid spoilage. Similarly, a company with efficient supply chain management practices may have a lower DIO than a company with less efficient practices. Measuring DIO can also help businesses make more informed decisions about their inventory investments. By analyzing DIO trends over time, companies can identify which products are selling quickly and which ones are not.
Understanding these effects aids in better financial planning and operational efficiency. That means we can easily say that day sales of inventory are one of the cash conversion cycle stages, which translates raw materials into cash. The job of every company is to transform the inventory into finished goods. Without having the finished goods in hand, the company won’t be able to sell and make money. That’s why an investor needs to look at the days a company takes to turn its inventory into sales. It is a financial measure, and it tells the investor how good the company is in handling its inventory.
